The Difference Between Online and Offline UPS Systems
-
In today’s technology-driven world, ensuring a steady power supply is crucial, especially for home users who rely on electronic devices for work, entertainment, or daily tasks. An Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) provides a vital solution by delivering continuous power during outages. Choosing the right UPS system—whether online or offline—can significantly impact your electronic equipment’s safety and functionality. This blog post will guide you through understanding the differences between online and offline UPS systems, helping you make an informed decision to secure your home power needs.
Overview of UPS Systems The Need for Uninterrupted Power Supply
In our tech-driven lives, power outages can cause data loss, damage to devices, or disrupt daily activities. A UPS system helps by giving you extra time to save your work, shut down devices safely, or keep things running smoothly. Power outages can lead to data loss, damage to devices, and interruptions in daily life.
A UPS system provides extra time to save your work, shut down devices safely, or keep things running. For home users, picking the right type of UPS—online or offline—is important. This choice helps avoid disruptions and costly issues.
The two main types of UPS systems, online and offline, cater to different needs and priorities. Online UPS systems offer continuous, clean power, making them ideal for sensitive electronics, while power inverter systems provide basic support, suitable for less critical applications. Understanding the nuances of each type is essential to match the UPS with your specific requirements.
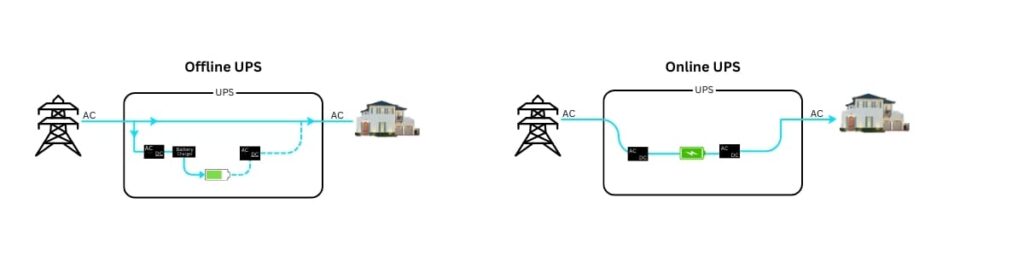
What is Online UPS?
Definition and Explanation What is Online UPS?
An power inverter, also known as a double-conversion UPS, is designed to provide an uninterrupted power supply by continuously converting incoming AC power to DC and then back to AC. This ensures that electronic devices receive a constant, stable power stream, free from fluctuations or interruptions. Online UPS systems are highly efficient in protecting sensitive equipment from power anomalies like voltage spikes, surges, and blackouts.
Online UPS Block Diagram Visualizing the Process Flow
To understand how an online UPS works, it’s helpful to visualize its power inverter. This system involves two key processes—rectification and inversion. First, incoming AC power is rectified into DC power, charging the battery and supplying power to the inverter.
The inverter then converts DC back to AC, providing a clean, stable power output to connected devices. This continuous conversion process ensures an unbroken power supply, even if the mains fail.
Key Features of Online UPS
Continuous Power Supply Without Switching
The primary advantage of an online UPS is its ability to deliver seamless power without any switching time, thanks to its double-conversion technology. This makes it ideal for critical devices like servers, medical equipment, and advanced home office setups that require an uninterrupted power source.
Higher Protection for Sensitive Equipment
Online UPS systems offer superior protection against power disturbances. By filtering out noise, voltage fluctuations, and transients, they safeguard sensitive electronic components, extending their lifespan and enhancing performance reliability.
What is Offline UPS?
Offline UPS Definition and Explanation.
An offline UPS, also known as a standby UPS, provides power backup by switching to battery power when it detects a disruption in the main power supply. Unlike online UPS systems, power inverter units are typically used for basic home appliances or devices that do not require constant power purity or zero transfer time.
Offline UPS Block Diagram How Offline UPS Works
The offline UPS block diagram illustrates its operational simplicity. Under normal circumstances, the UPS allows raw AC power from the wall outlet to directly power connected devices. When an outage or significant fluctuation is detected, the system switches to battery power, supplying energy through an inverter until the main power is restored, at which point it reverts to normal mode.
Key Features of Offline UPS
Switches to Battery Power During Outages
The main feature of an offline UPS is its ability to switch to battery backup during power outages, providing temporary power to save work and safely shut down devices. While there is a slight delay during the switch, this option is sufficient for non-critical applications like home entertainment systems or basic computer setups.
Suitable for Basic Home Appliances
Offline UPS systems are cost-effective solutions for protecting against power interruptions in environments where continuous power is not critical. They are typically more affordable and easier to maintain than online UPS systems, making them ideal for households with less demanding power requirements.
Difference Between Online and Offline UPS
Difference Between Online and Offline UPS Key Differences Explained
Understanding the difference between online and offline UPS systems is key to selecting the right one for your needs. While both serve the essential function of providing backup power, their operation, efficiency, and suitability vary significantly.
Power Supply Continuity
Online uninterruptible power supplies continuous power supply through their double-conversion process, ensuring zero transfer time during outages. In contrast, offline UPS systems have a brief delay during the switch to battery power, which may not be suitable for devices requiring uninterrupted service.
Efficiency and Power Consumption
Offline UPS systems are generally more energy-efficient in normal operation due to their direct connection to the mains power. In contrast, online UPS systems continuously process power, resulting in higher energy consumption and operating costs. This trade-off is often justified for mission-critical applications where power quality and consistency are paramount.
Protection Level
In terms of protection, online UPS systems provide superior safeguards against electrical disturbances, offering a cleaner power output ideal for sensitive equipment. Offline UPS systems provide basic protection, sufficient for less critical devices but potentially inadequate for high-end electronics.
Online UPS vs Offline UPS - Which One to Choose?
Detailed Comparison Online UPS vs Offline UPS
Choosing between an online UPS and offline UPS depends on your specific power protection needs and budget considerations. Online UPS systems are ideal for environments where power quality is critical, while offline systems suffice for standard home use with basic backup requirements.
Suitability Based on Requirements Home vs Commercial Use
For home users, offline UPS systems offer adequate protection at an affordable price point for devices like computers, modems, and TVs. However, for those working from home or using high-performance electronics, an online UPS provides the necessary reliability and protection.
Online UPS and Offline UPS When to Opt for Each Type
Opt for an online UPS if you need uninterrupted power for sensitive systems, or work in areas prone to frequent power fluctuations. Offline UPS systems are best for general household use, providing a reliable backup without the higher cost associated with online models.
Understanding the Block Diagram of Online and Offline UPS
A Deeper Look at the Online Offline UPS Block Diagram
By examining the power inverter, users can better understand how these systems operate under different circumstances. Each diagram highlights the distinct pathways and components that ensure uninterrupted power delivery.
Visuals to Explain How Each UPS Works in Different Scenarios
Visual aids can effectively illustrate the operational differences between online and offline UPS systems, depicting scenarios such as normal operation, power loss, and recovery. These visuals serve as educational tools for users to grasp the mechanics of each system.
Highlight the Functionality of Bypass Mode in Online UPS
One notable feature of online UPS systems is the power inverter, which allows the system to run on raw mains power during maintenance or in the event of an internal fault. This ensures continuity while minimizing downtime, a critical aspect for businesses and tech-savvy home users.
Conclusion
Recap Key Differences and Use Cases of Online and Offline UPS
In conclusion, both online and offline UPS systems play crucial roles in maintaining power continuity. Online UPS systems offer high levels of protection and reliability for sensitive equipment, while offline systems provide cost-effective solutions for basic home applications. Understanding the difference between online and offline UPS is vital for making power inverter tailored to your power needs.
Final Recommendations Choosing the Right UPS Based on Need
When choosing a UPS, consider your specific requirements, the criticality of your devices, and your budget. For those seeking maximum protection and reliability, an online UPS is the ideal choice. For general home use, an offline UPS offers a balance of efficiency and affordability. Whichever you choose, power inverter ensures your devices remain protected, and your lifestyle uninterrupted.






