Fracture Of The Greater Tuberosity: Mechanism Of Fracture
This type of fracture occurs in the following cases of direct and indirect injury.
In cases of a direct injury, the patient falls with the arm in an abducted position. Here, the force is transmitted in an upward direction along the humerus (the long bone in the upper arm). The greater tuberosity encroaches against the acromion process which further leads to the upper end of the humerus fracture.
In other cases, such fractures can occur due to an indirect injury which usually happens before the epiphyseal union. Sudden contraction of the supraspinatus muscle (supraspinatus is a relatively small muscle of the upper back) can produce separation of the greater tuberosity. In the adult age group, the same contracting force the supraspinatus muscle can lead to tearing of the supraspinatus tendon. Our company manufactures Locking Distal Humerus Plate Medial Side 2.7 / 3.5mm for distal humerus fracture.
Diagnosis
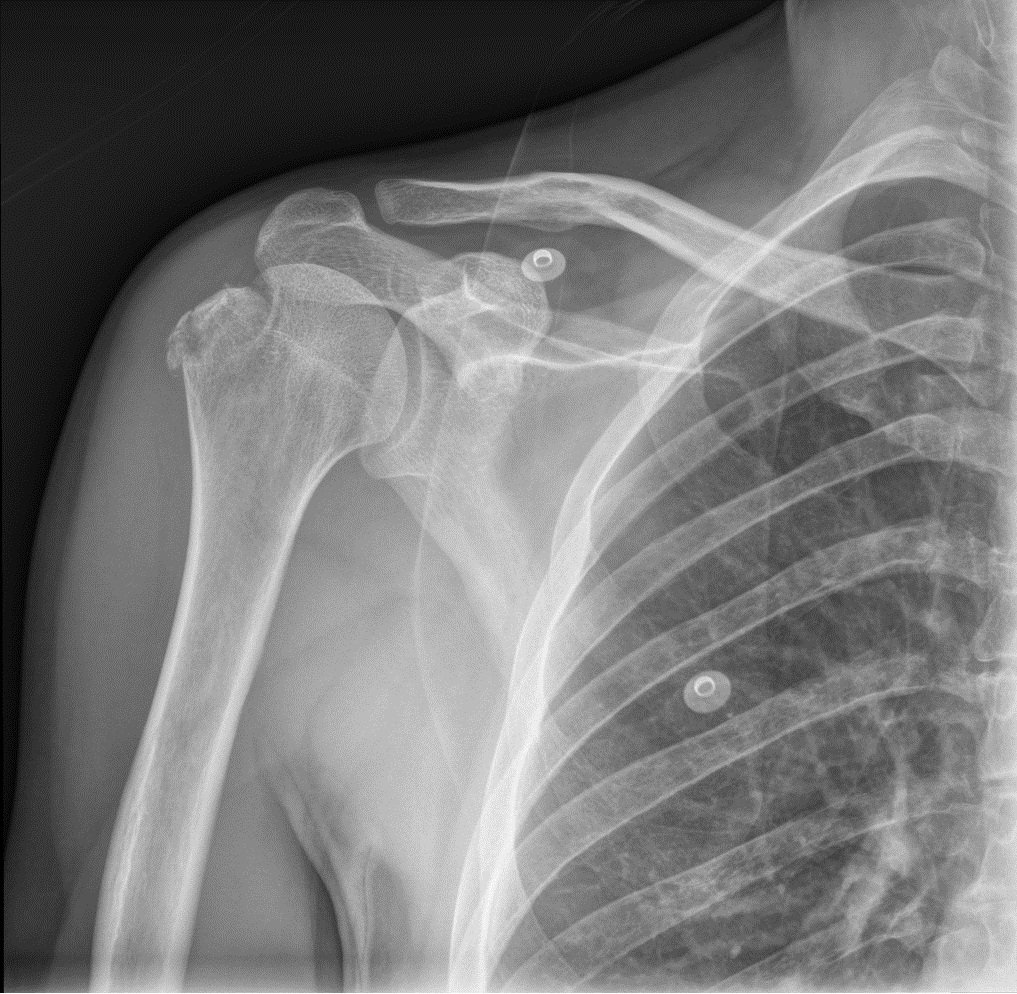
Proper diagnosis is very important in all kinds of fractures. Some of the common symptoms that patients often complaints include pain and swelling around the shoulder area. Also, the abduction movement is painful, restricted, or absent X-ray diagnosis or Radiological evidence substantiates the fracture.
While going through the X-ray diagnosis, two views should be taken. Further, the amount of parting of the greater tuberosity must be considered cautiously.
The lesion in case of fracture of the upper end of the humerus can be of the following five types.
I. Fracture without displacement.
II. Nominal displacement of the fragment.
III. Comminuted fracture without displacement.
IV. Under the acromion process, a small piece of bone is pulled upwards
V. Fracture with a coarse displacement of a large piece of bone.
Treatment
In the case of fracture of the upper end of humerus, it is very important to diagnose the condition early and properly. If the condition is not recognized and properly treated, a disability may appear like the abduction disability of the shoulder.
The treatment varies as per the diagnosis. In cases where there is no displacement, a reduction is not required. A simple cuff and collar sling which provides more mobility is useful. Doctors generally prescribe an early exercise of the joints of the limb.
In patients where displacement is there in fracture diagnosis, reduction, as well as maintenance of this reduction of the fracture, is fundamental.
Orthopedic implants experts also use conservative treatment in such cases. In this type of treatment, the affected limb is immobilized in an orthopedic implant like an abduction splint or a plaster spica. It is used to provide an abduction of 30, 60 & 90 degrees. Here, the shoulder is maintained at 90° abduction, 60° external rotation, and 40° forward fixed position. An X-ray of the joint is then done to confirm the reduction. Besides this, immobilization or restriction in movement is continued for a period of six weeks.
An operation may also be needed in some cases as discussed below
In the first case, where there is a failure of closed reduction, fixation of the tuberosity by suture or screw may be required.
While on the other hand, in some other cases where the fragment is small, it should be excised and the supraspinatus tendon which passes laterally beneath the cover of the acromion is sutured to the humerus.
Lastly, the after-treatment involves the immobilization of the arm in an abduction splint.