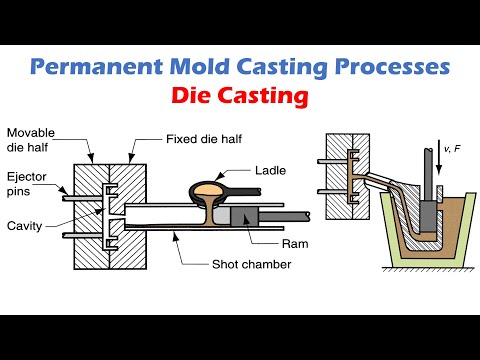
What is Aluminum Heat Treating for Alloy Castings and Why Do You Need It
Cuerpo
It is the goal of today's blog post to describe aluminum heat treating, how it can benefit your aluminum cast, and how our Denver-area foundry can assist you with your aluminum casting requirements.
When it comes to aluminum heat treatment, what exactly is it and how does it work?
Through the application of heat, aluminum alloy casts can be made stronger and more structurally stable, making them more suitable for use in aerospace and defense applications. After being heated to a specific temperature, the strength of an aluminum alloy cast is measured on a scale ranging from T1 to T10, which indicates the tempered strength of the cast after it has been heated. As the T-number rises, the length of the process, as well as the amount of stretching, compressing, and other processes, are lengthened and repeated more frequently, resulting in a longer process and more processes being repeated.
An advanced heat treatment process at junying produces the T-6 temper code in two steps. As a result, the alloy can be strengthened by up to 30%, depending on the application.
Even though there are a number of different repeated steps in the aluminum heat-treating process, in actuality, there are only two differentiated steps that are used to harden the aluminum alloy cast — quenching and aging.
What Is the Definition of Quench Hardening?
In the manufacturing industry, quenching refers to the process of rapidly cooling a cast or machined part by immersing it in water for an extended period of time. A prototype's quenching process involves rapidly heating the metal and maintaining die casting China at a high temperature for an extended period of time, though the exact procedure will vary depending on the size and type of the prototype. In this case, variables such as time and temperature are determined by the precise size and composition of each prototype, which means that precise measurements will differentiate between different pieces.
After the materials have been heated for a period of time, the prototype is removed from the oven and placed on a work surface. After the product has been heated for the desired amount of time, it is quickly cooled using a liquid bath or, in some cases, an air furnace, depending on the application. Even after soaking or remaining in the air furnace for an extended period of time, the prototype can be removed and allowed to cool further before being immersed in quenching fluid (typically water) until it is completely cooled down.
What is the method by which quenching accomplishes its goal?
Even though quenching is a necessary step in the hardening process, the true purpose of this step is not as obvious as it first appears. Quenching can change the structure of crystal structures in some metals, making them harder. When it comes to aluminum, however, the quenching process is a little more difficult to understand. As a result of quenching aluminum, all of the alloying elements are dissolved into a solid solution within the aluminum, resulting in an increase in the aluminum's strength. After that, it'll be time to put it through its paces again.
What is the process of aluminum aging and how does it work?
Aging is a technique for physically strengthening metals, including aluminum alloys, by exposing them to air for an extended period of time. Ageing can also impart different properties to metals, such as high coercivity, which is also known as a reduction in the magnetization of the metal, and other properties, in addition to strengthening the metals.
When the aging process begins, the alloy is baked at a low temperature for up to ten hours, depending on its composition, in an oven at a low temperature. The piece is then allowed to cool naturally, allowing it to become precipitation hardened as a result of the cooling process. Copper aluminum crystalline structures are formed as a result of the heating and cooling processes used in their production. Temperature at which the prototype was aged, as well as the length of time that the prototype was aged, can both influence the size and shape of the crystalline structures. Higher-quality finished products are produced by using larger crystalline structures, whereas lower-quality finished products are produced by using smaller crystalline structures.











Comentarios