-
 Retrouver dansMembres
Retrouver dansMembres Retrouver dansVidéos
Retrouver dansVidéos Retrouver dansChaînes
Retrouver dansChaînes
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
To learn more about our privacy policy Cliquez iciPréférence de confidentialité
- Mots clés - #Attune Hearing clinic
-
- Dernière mise à jour 17 février 2022 0 commentaire , 163 vues, 0 comme
More from Attunehearing Attunehearing
More in Politics
Related Blogs
What is sensorineural hearing loss?
Posté par Attunehearing Attunehearing
17 février 2022
Corps
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most frequent hearing impairment type. Every individual has their own set of hearing thresholds that will never change. However, harsh or loud noises can damage hair cells in the inner ear. The hair cells are responsible for sending sound signals to the brain. Other causes of hair cell damage include poor nutrition, too many colds in a row, and repeated infection from waterborne pathogens like meningitis.
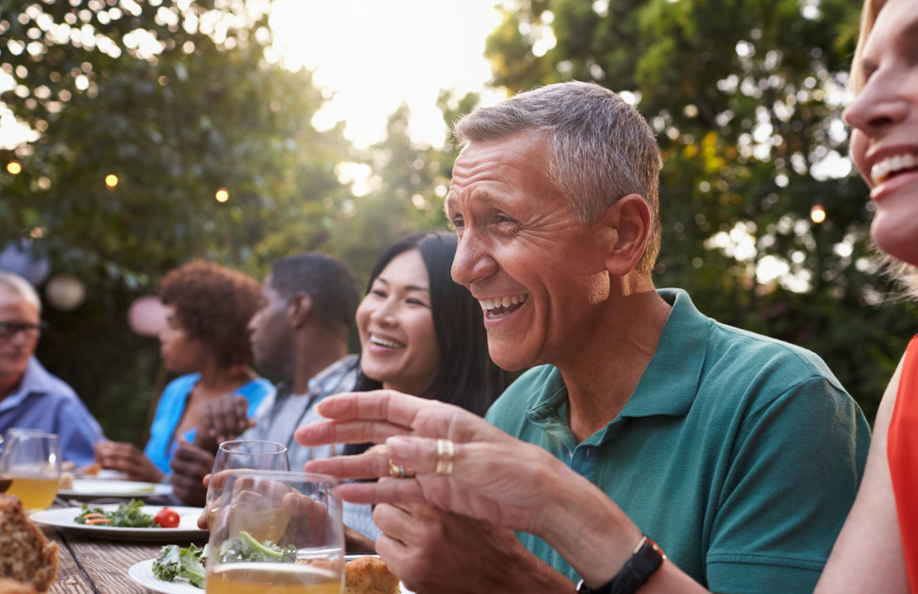

Hair cell damage can lead to hearing loss in high frequencies. This is often the result of exposure to loud noises, especially at a young age. An individual may have additional conductive hearing loss (damage to their middle or outer ear) or some combination of both types of hearing loss.
Hearing impairment may cause speech difficulties and affect the ability to learn and interact with others contributing to social isolation. Fortunately, most sensorineural hearing loss cases can be controlled with a medical intervention using the latest technology.
There are two main types of sensorineural hearing loss: peripheral and central.
Peripheral hearing loss occurs when hair cells are damaged due to exposure to loud noises, resulting from an ear infection or high-level noise trauma. Hairs may grow back, and the ear can start to heal itself.
However, in most cases, one will notice hearing impairment. It is essential to get checked by a doctor if one has an ear infection or any kind of skin irritation in their ear. It may not be a hearing loss, but it could be an infection, and an individual will most likely not know until they get the proper treatment.
Central hearing loss occurs when hair cells are damaged due to ageing or disease. This type of hearing impairment is harder to treat, significantly if a person has advanced age. A central hearing loss may affect more than one ear, so it is essential to determine which ear is affected. This can be done by using a stethoscope if only one ear is affected. If both ears are affected, an audiologist should perform hearing tests.
If you think you may have hearing loss, book a hearing test at your nearest Attune Hearing clinic. Visit their website for more information or to book an appointment.






commentaires