What are Standards and Types of Aerospace Fasteners
الجسم
In the intricate world of aviation manufacturing, aerospace fasteners play a crucial role in connecting myriad components of an aircraft, facilitating load transfer, and coordinating deformation during loading. This article delves into the standards governing aerospace fasteners and explores various types of nuts, washers, and screws commonly used in the aviation industry.
Standards for Aerospace Fasteners:
NAS (National Aerospace Standards):
NAS stands as the most influential standard for British fasteners in aviation manufacturing. It extends its coverage not only to commercial aircraft but also to military aircraft.
NASM (National Aerospace Standards Community):
Originally a military standard, NASM has transitioned into NASC (National Aerospace Standards Community) for continuous maintenance and development, essentially serving as the military standard within NAS.
NA / NAM:
NA corresponds to NAS standards, while NAM corresponds to NASM, both being public products associated with specific standards.
Common US Government Standards:
In addition to British standards, several US government standards are prevalent in the aerospace industry, such as MS and AN. MIL, the US military standard, is often used to define more detailed technologies.
Aerospace Nuts:
Standard Aerospace Nuts include:
AN310 Castle Nut: Used in conjunction with AN3 to AN20 bolts, with materials like nickel alloy steel, stainless steel, and 2024 aluminum alloy.
AN320 Shear Castle Nut: Specifically designed for shear stress applications, used with AN2L to AN36 shaft pin bolts, primarily made of 2024 aluminum alloy.
AN315 Ordinary Nut: Used for parts subject to large tension, requiring anti-loose nuts or spring washers for fastening. Materials are similar to AN310 nuts, with both right-hand and left-hand threads available.
AN316 Lock Nut: A hexagonal lock nut adopting double nuts to prevent loosening, typically used with AN315 ordinary nuts.
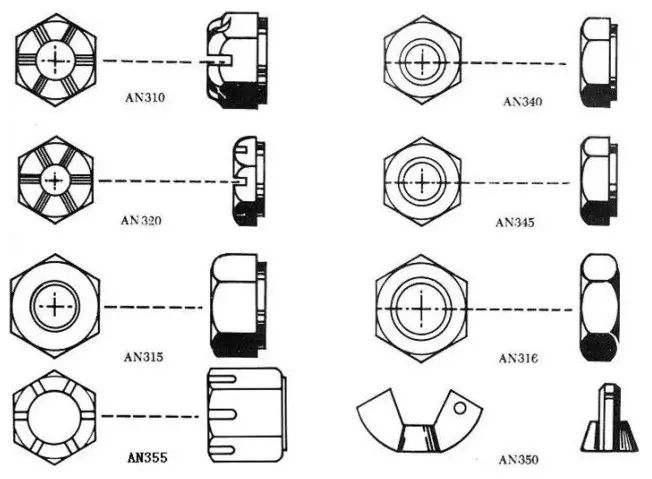
Self-Locking Nuts:
Low-temperature self-locking nut models AN365 and AN364.
High-temperature self-locking nut model AN363.
Both types utilize elasticity to prevent loosening and are suitable for repeated use.
Aerospace Washers:
AN960 is a widely used standard aerospace washer, employed under hexagonal nuts, and is available in various materials such as carbon, steel, brass, stainless steel, and aluminum alloy. AN936 washers offer uniform elasticity and effective anti-loosening properties.
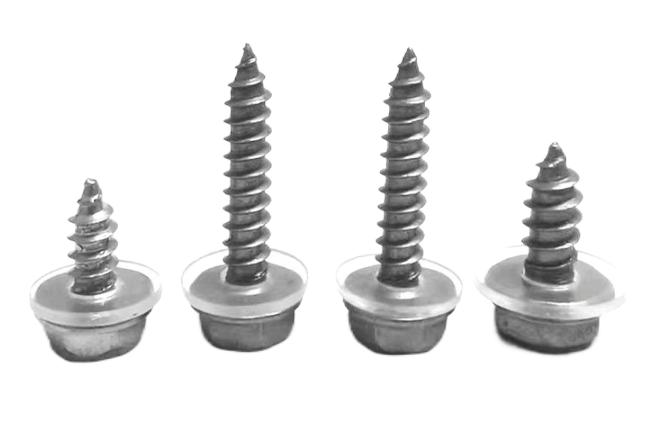
Aerospace Screws:
Categorized into mechanical screws, structural screws, and self-tapping screws, aerospace screws serve non-structural connections, fairings, and removable panels in non-main stressed structures.
Mechanical Screws:
Common models include AN500 and AN501 (coarse and fine round head screws), AN505 and AN507 (coarse and fine 82° countersunk screws), and AN515 and AN526 (coarse and fine round head screws).
Structural Screws:
AN509 (100° flat screw), AN525 washer head screw, AN502, and AN503 (round head screws) are among the common models. Structural screws, made of alloy steel, can be used as a structural bolt due to their polished rod section.
Self-Tapping Screws:
Characterized by fastening through tapping, self-tapping screws like AN504 and AN506 (for removable parts) and AN530 and AN531 (for metal plates) come in flat round head, 100° countersunk head, and large flat round head types.

Conclusion:
This article provides an overview of the fundamental aspects of aerospace fasteners, encompassing standards and various types of nuts, washers, and screws employed in the aviation manufacturing industry. Understanding these components is essential for ensuring the structural integrity and safety of aircraft.








تعليقات