Unveiling the Importance: Mitochondrial DNA and Inherited Diseases
Body
Mitochondria DNA (mtDNA) plays a crucial role in the inheritance of certain diseases, shedding light on the complex interplay between genetics and health. Understanding the role of mtDNA in inherited diseases is essential for diagnosing, treating, and preventing these conditions. Let's explore how mtDNA influences inherited diseases and its significance in medical research and healthcare.
The Basics of Mitochondria DNA
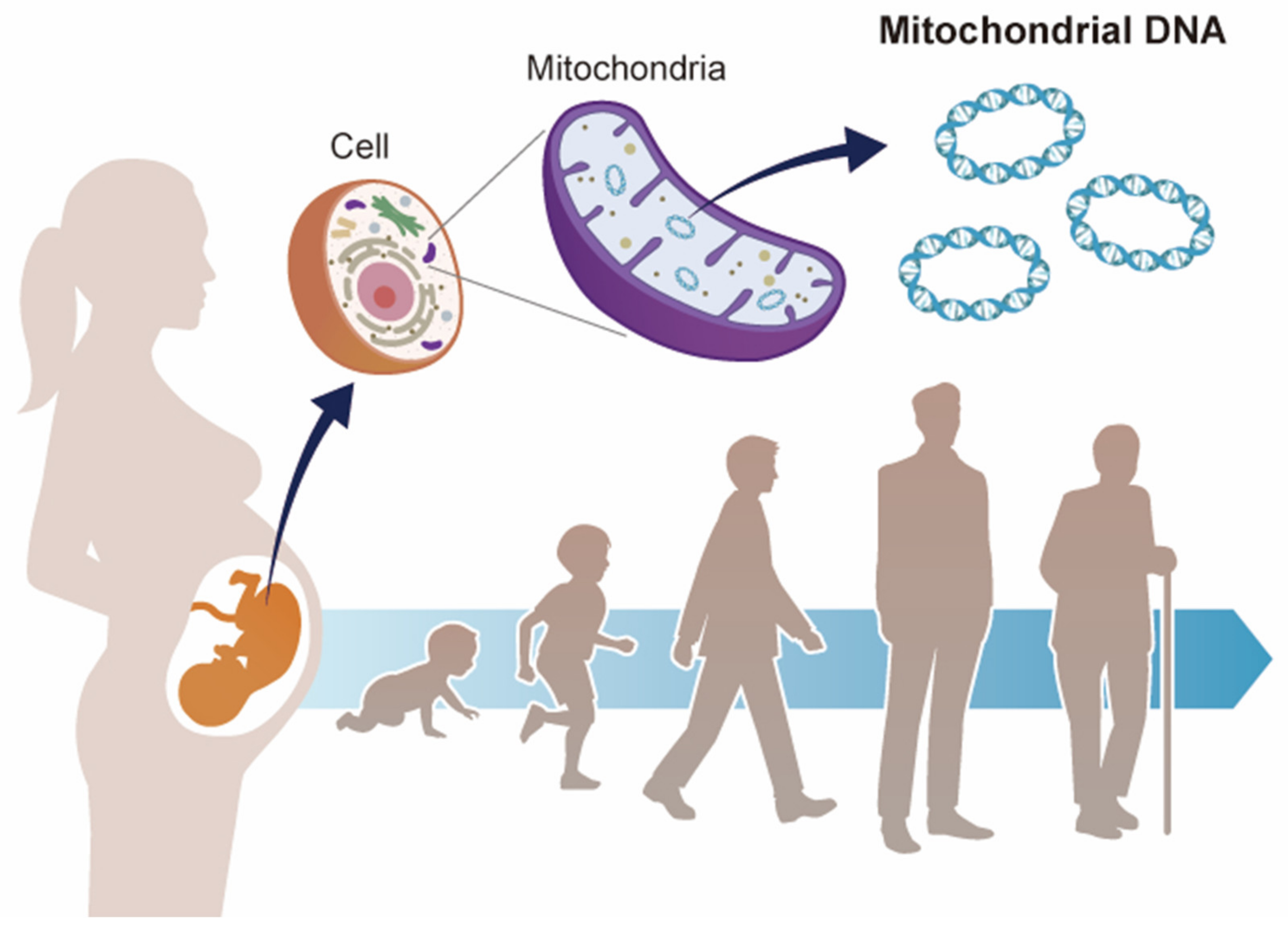
Mitochondria https://tendna.com/en/disease/mitochondria are small organelles within cells that produce energy essential for cellular function. Unlike nuclear DNA, which is inherited from both parents, mtDNA is solely passed down from the mother to her offspring. This unique inheritance pattern makes mtDNA particularly susceptible to mutations and genetic variations that can impact health and disease.
Mitochondrial Inheritance: Understanding the Mechanisms
Inherited diseases associated with mtDNA mutations are often passed down in a maternal inheritance pattern. This means that affected individuals inherit the mutated mtDNA from their mother, who may or may not exhibit symptoms of the disease. The severity and presentation of inherited mitochondrial diseases can vary widely, depending on factors such as the type and location of the mutation and the proportion of mutated mtDNA within cells.
Common Inherited Diseases: Examples and Symptoms
Several inherited diseases are associated with mtDNA mutations, ranging from mitochondrial myopathies to neurodegenerative disorders and metabolic syndromes. Examples include:
- Mitochondrial myopathy: Characterized by muscle weakness, fatigue, and exercise intolerance.
- Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON): Causes vision loss, particularly in young adults.
- Leigh syndrome: Affects the central nervous system, leading to developmental delays, movement disorders, and neurological deterioration.
These inherited diseases can have a significant impact on quality of life and may require lifelong management and care.
Diagnostic Challenges: Identifying Mitochondrial Diseases
Diagnosing mitochondrial diseases can be challenging due to their diverse symptoms and genetic heterogeneity. Traditional diagnostic methods include biochemical assays, muscle biopsies, and genetic testing to detect mtDNA mutations. However, advances in genetic sequencing technologies have enabled more accurate and comprehensive diagnosis of mitochondrial diseases, allowing for personalized treatment and management strategies.
Treatment Approaches: Managing Mitochondrial Diseases
While there is currently no cure for most mitochondrial diseases, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. This may include:
- Medications: Such as antioxidants, vitamins, and supplements to support mitochondrial function.
- Physical therapy: To improve muscle strength and mobility.
- Symptom management: Addressing specific symptoms such as vision loss or neurological impairment.
In some cases, experimental treatments such as gene therapy or mitochondrial replacement therapy may offer potential avenues for future intervention.
Future Directions: Research and Therapeutic Advances
Ongoing research into mitochondrial biology and genetics holds promise for understanding the underlying mechanisms of mitochondrial diseases and developing targeted therapies. Emerging technologies such as gene editing and mitochondrial replacement techniques offer new possibilities for treating and preventing inherited mitochondrial disorders. Additionally, collaborative efforts among researchers, clinicians, and patient advocacy groups are essential for advancing knowledge and improving outcomes for individuals affected by mitochondrial diseases.
Conclusion: Mitochondria DNA and Inherited Diseases
In conclusion, mitochondria DNA plays a critical role in the inheritance of certain diseases, providing insights into the genetic basis of inherited mitochondrial disorders. Understanding the mechanisms of mitochondrial inheritance and the impact of mtDNA mutations on health and disease is essential for diagnosing, treating, and preventing mitochondrial diseases. While challenges remain in diagnosis and treatment, ongoing research and therapeutic advances offer hope for improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals affected by inherited mitochondrial disorders.











Comments